Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Infusion Therapy
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma is a type of cancer that begins in the lymphatic system, affecting white blood cells called lymphocytes. It can develop in lymph nodes, other lymph tissues, or organs throughout the body. The disease varies in aggressiveness, with some forms growing slowly and others progressing rapidly. Symptoms often include swollen lymph nodes, fatigue, and unexplained weight loss. Treatment typically involves chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or immunotherapy, depending on the specific subtype and stage of the disease.
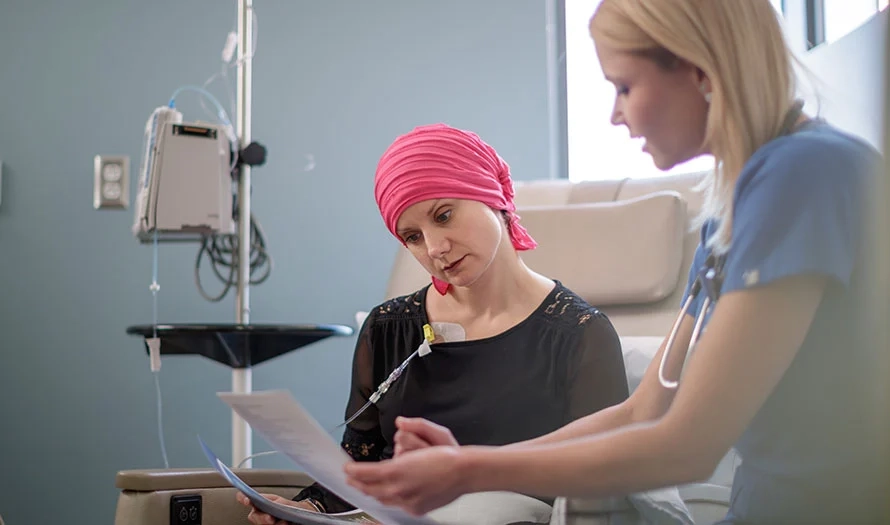

Symptoms
Symptoms
Here are the common symptoms of Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma:
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck, armpits, or groin
- Persistent fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fever
- Night sweats
- Chest pain or pressure
- Abdominal pain or swelling
- Shortness of breath
- Cough
- Itchy skin
- Loss of appetite
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- Less common symptoms may include:
- Neurological changes (if the cancer affects the brain)
- Bone pain
- Skin rashes or lesions
It's important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions. If you experience persistent symptoms, especially swollen lymph nodes or unexplained weight loss, it's advisable to consult a healthcare professional.

Treatment Options
Here are the main treatment options for Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma:
- Chemotherapy:
- Uses drugs to kill cancer cells
- Often the primary treatment
- Radiation therapy:
- Targets cancer cells with high-energy beams
- May be used alone or with chemotherapy
- Immunotherapy:
- Boosts the body's immune system to fight cancer
- Includes monoclonal antibodies and CAR T-cell therapy
- Targeted therapy:
- Drugs that attack specific cancer cell features
- Stem cell transplant:
- Replaces diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells
- May be autologous (patient's own cells) or allogeneic (donor cells)
- Watchful waiting:
- For slow-growing lymphomas, treatment may be delayed until necessary
- Surgery:
- Rarely used, mainly for biopsy or treating certain complications
- Clinical trials:
- Access to new, experimental treatments
Treatment plans are individualized based on the lymphoma type, stage, and patient's overall health.

Living With
Living with Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma involves managing the disease and its effects on daily life. Patients often need to attend regular medical appointments for treatments and check-ups. Side effects from treatments like fatigue, nausea, and weakened immunity require lifestyle adjustments. Maintaining a healthy diet and getting enough rest become crucial. Many patients find support groups helpful for emotional well-being. Exercise, when approved by doctors, can improve energy levels and mood. Stress management techniques like meditation or counseling may be beneficial. Some patients might need to modify work schedules or responsibilities. It's important to communicate openly with healthcare providers about symptoms or concerns. Despite challenges, many people with Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma lead fulfilling lives, especially with advances in treatment options and supportive care.
Meet our Infusion Specialists
Jalal Thwainey M.D.
Medical Director
Emilie Wojcik, N.P.
Director of Clinical Services
For Provider
Simplify patient referrals and offer advanced treatment options with our infusion partnership program.
For Patient
There may be a better way to manage your condition – explore infusion therapy.





